3D Waveguide Example using ToyFDTD code and the DAB/CRBC Library¶
For this example, we use ToyFDTD2
and add the functionality of the DAB/CRBC library. ToyFDTD was originally
written by Laurie E. Miller, it is no longer maintained but has been archived
by Doug Neubauer.
The original file for this example can be downloaded at here.
The modified version with DAB/CRBC library can be download at ToyFDTD_CRBC.tar.gz.
Instead of rewriting the original ToyFDTD2 file, we write a seperate file called external_c_codes.c to control most of the CRBC setting and user-defined functions.
To compile and run the program(specify the location of CRBC library i.e. the directory containing libyeecrbc.a):
setenv yeecrbc_DIR ~/YeeCRBC/lib
make
./run.x
Use CRBC library in the Yee scheme¶
The CRBC libary is initialized before the time stepping begins
void *ptr_crbc;
crbc_init(&ptr_crbc,dx,dy,dz,nx,ny,nz,ioff_ex,ioff_ey,ioff_ez, MAXIMUM_ITERATION, dt, LIGHT_SPEED);
char vtkfilename[256];
FILE *f;
for(iteration = 0; iteration < MAXIMUM_ITERATION; iteration++)
{// mainloop
...
}
Basic information if passed from Yee Scheme solver to CRBC through crbc_init(). All CRBC related information can be accessed through the pointer ptr_crbc. ioff_ex, ioff_ey, ioff_ez defines the leading dimension of the E field arrays, since in the ToyFDTD2, the Ex, Ey, Ez file are defined as the following
#define Ex(I,J,K) ex[ioff_ex*(I) + (nz+1)*(J) + (k)]
#define Ey(I,J,K) ey[ioff_ey*(I) + (nz+1)*(J) + (k)]
#define Ez(I,J,K) ez[ioff_ez*(I) + nz*(J) + (k)]
off_ex = (ny+1)*(nz+1);
ioff_ey = ny*(nz+1);
ioff_ez = (ny+1)*nz;
ex = calloc(nx*(ny+1)*(nz+1),sizeof(double));
ey = calloc((nx+1)*ny*(nz+1),sizeof(double));
ez = calloc((nx+1)*(ny+1)*nz,sizeof(double));
The actual computation of the CRBC is done at the end of the time iteration:
computeboundary(ex,ey,ez,&ptr_crbc);
}// end mainloop
We add the variable vtkfilename to hold the filenames for VTK files output, and use writeefield() to write the VTK files to the disk. These utility functions are defined in external_c_codes.c and can be called in the following way
sprintf(vtkfilename,"CRBC_%08d_Ez.vtk",iteration);
writeefield(ex,ey,ez,3,&ptr_crbc,vtkfilename);
Setup CRBC¶
In external_c_codes.c, we need to set at which we are going to apply CRBC. This is done in crbc_init():
d->boundaries[CRBC_XLeft] = CRBC_PEC;
d->boundaries[CRBC_XRight] = CRBC_CRBC;
d->boundaries[CRBC_YLeft] = CRBC_PEC;
d->boundaries[CRBC_YRight] = CRBC_PEC;
d->boundaries[CRBC_ZLeft] = CRBC_PEC;
d->boundaries[CRBC_ZRight] = CRBC_PEC;
In this case, only the X+ side is an open end, the rest of the boundaries are all PEC. If we want to do a free space scattering problem, we just need to change all boundaries to ‘CRBC_CRBC’. In order to obtain a reliable error bound for long time simulation, the CRBC library need to know the total time(=MAXIMUM_ITERATION*dt) and the initial distance from the source to the CRBC faces. The latter is set in setup_crbc():
// Now set up the faces. Start by looping over all of the possible faces. We
// follow the order given in CRBC_Side, so
// l = 0 --> CRBC_XLeft
// l = 1 --> CRBC_XRight
// l = 2 --> CRBC_YLeft
// l = 3 --> CRBC_YRight
// l = 4 --> CRBC_ZLeft
// l = 5 --> CRBC_ZRight
for (l=0; l<6; ++l) {
// First we need to calculate the minimum distance between the boundary and
// source. Since we placed the source in the center of the domain, this is
// simple. If it is not possible to calculate this directly, using a lower
// bound for the seperation is the safest thing to do, but it may result
// in more work being done that is actually needed to achieve the desired
// accuracy.
switch (l / 2) {
case 0: // Faces with a normal in the x-direction
delta = (d->imax / 1.0) * (d->dx);
break;
case 1: // faces with a normal in the y-direction
delta = (d->jmax / 2) * (d->dy);
break;
case 2: // faces with a normal in the z-direction
delta = (d->kmax / 2) * (d->dz);
break;
}
The modified Yee solver communicates with CRBC library through one layer of data, whose indices are defined in:
crbc_low_index[];
crbc_high_index[];
These indices are defined each CRBC face on all three E field components.
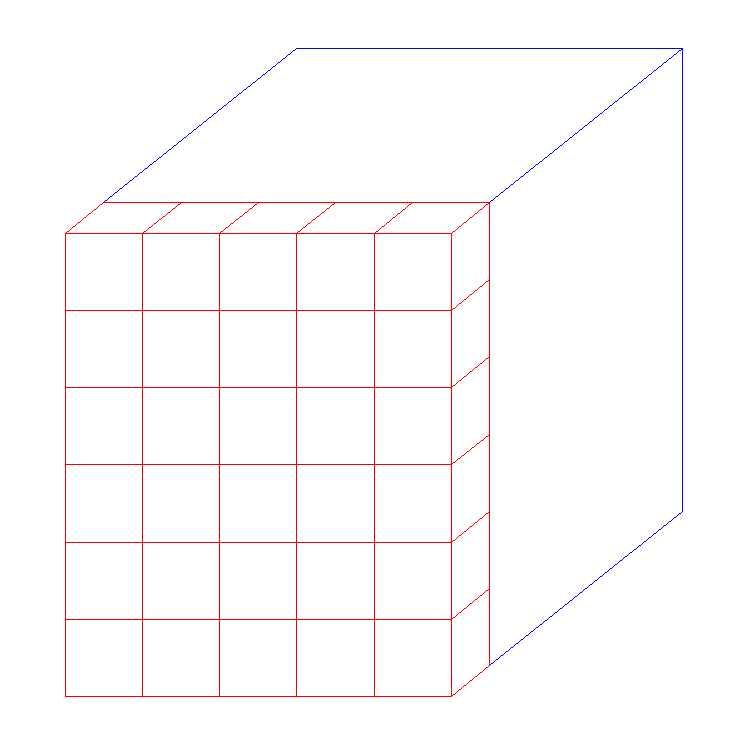
One layer of Yee cell data to communicate with CRBC library.¶
On each Yee cell, the field variables are defined as shown below.
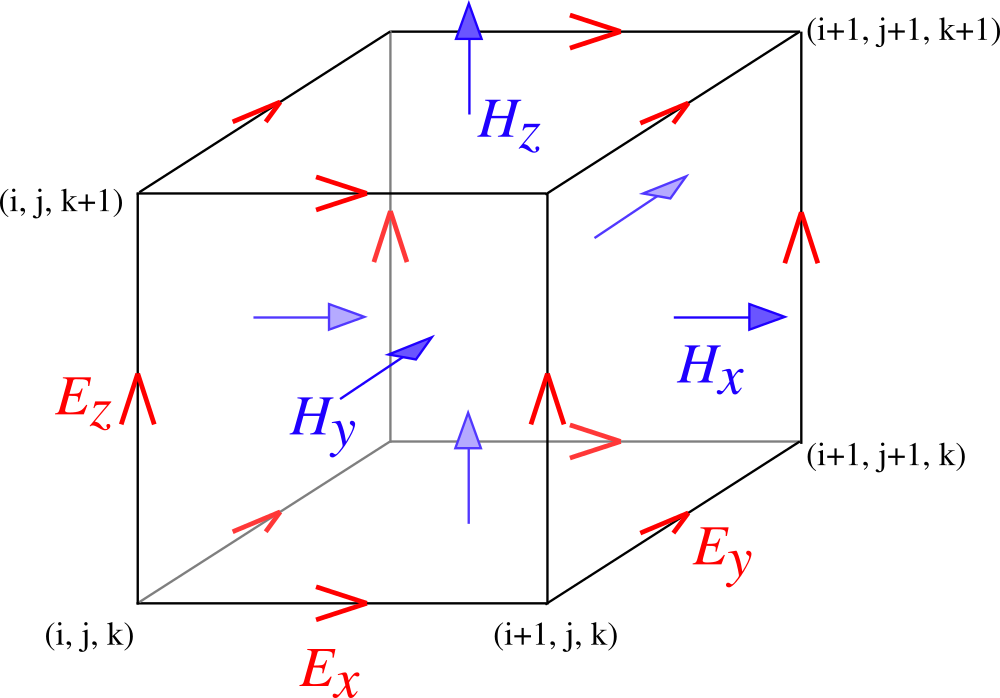
Spatial configuration of a Yee cell.¶
Outputs¶
The output VTK files can be viewed in Paraview and the following movie was generated by cutting out a strip of the wave guide.
More Information¶
For more detailed information about implementing the DAB/CRBC library in 3D with the Yee scheme, please refer to 3-D FDTD code with CRBC/DAB Boundary Conditions.